One of the important things during the development of industrial solutions and machinery and equipment is the prototyping, testing, and manufacturing of final products. It is worthwhile to optimize the production costs of individual components, and this can be done, among others, by using a cheaper method of production. We compared two methods - CNC technology and 3D printing. How do they differ?
Subtractive manufacturing or 3D printing?
3D printing is additive manufacturing in which the model is created by applying layers of the filament. CNC milling machines are a cavity technology in which the tools pull the layers of material, shaping the previously programmed model. Both these techniques make it possible to obtain a physical product, but both the process of its preparation, as well as costs, production time and durability are different. Which method is more beneficial? It all depends on the purpose of using the model, its utility and budget.
Type of material
The CNC milling machine allows us to obtain the final model from many different types of materials - metal alloys, plastic, or wood. In the case of 3D printers, it is necessary to use one type of material (depending on the device technology) prepared in a form appropriate for the application. However, it is worth noting that there are many types of printing materials. They differ in their properties, so they can be selected for a specific implementation depending on the purpose of use. The most common 3D printing technology is FDM, which is based on production from plastic (e.g. PLA, ABS, Nylon, or TPU). Comparing the production on CNC milling machines and 3D printers in FDM technology, it is possible to specify many advantages of both technologies, however, in case of using different types of materials within one device, CNC gains the advantage.
Durability
Comparing the execution of a detail made of aluminum (metal) and PLA (plastic), one can assume that models made on CNC will be much more durable. However, when making a prototype or an element from which we will not require mechanical or thermal resistance, will the aspect specified be significant?
High-quality elements printed in 3D technology can be obtained cheaply and quickly and used not only during tests but also implemented in the finished product. Models made of plastics will also be lighter.
Speed of production and operator work
Although the total machine time is longer for 3D printing, manufacturing on CNC machines, in addition to machining, requires the continuous presence of the operator and his greater involvement in the entire process. A well-prepared model for printing and properly selected parameters of the device reduces to a minimum the operation of the 3D printer and, consequently, the time of the whole process.
Costs of making a single model
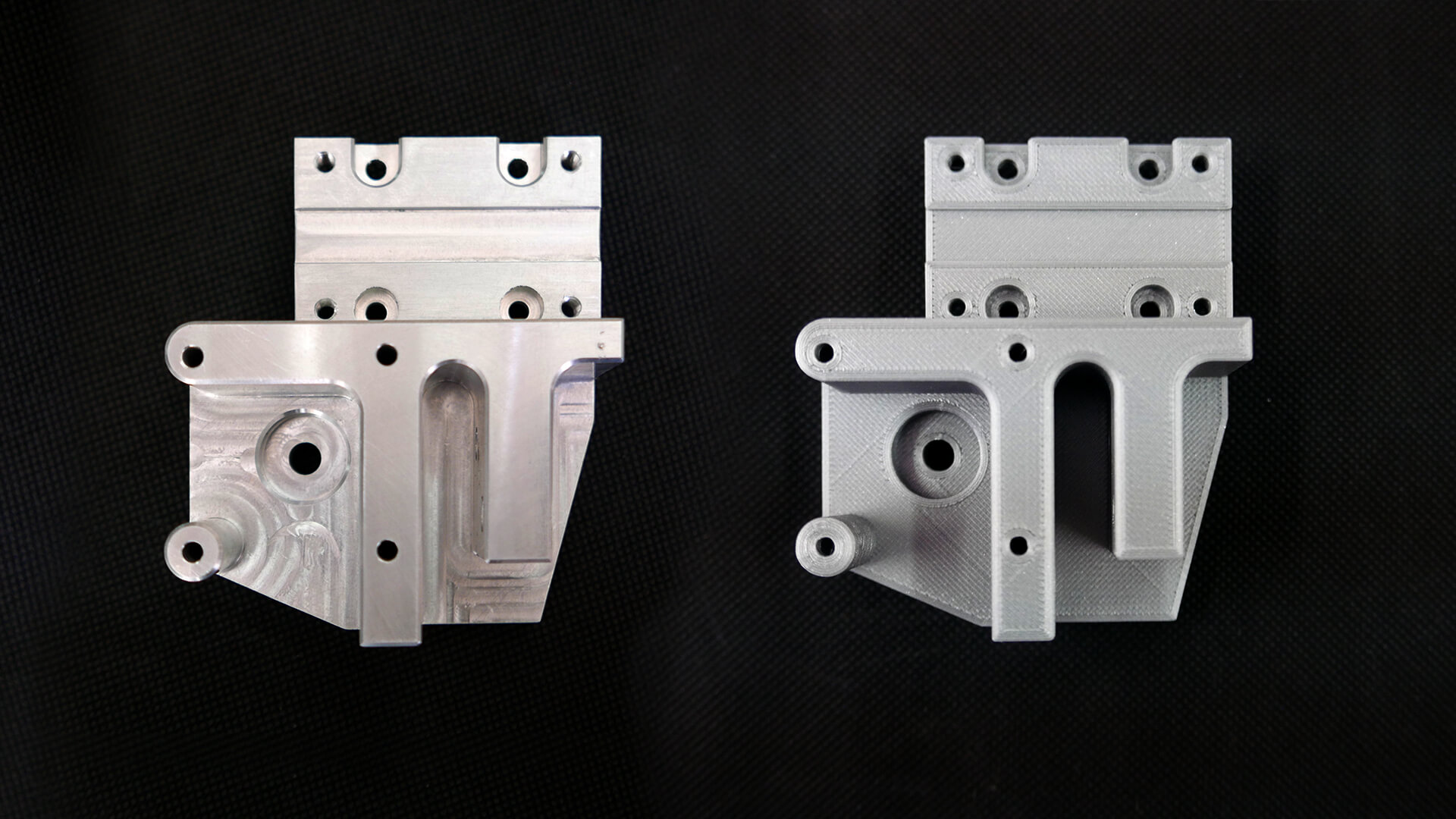
In order to analyze production costs, we have created comparative models - one in 3D printing technology, the other one processed on a CNC machine. Below we present their characteristics. The obtained results showed that creating a model on a 3D printer is four times cheaper than machining on a CNC milling machine.
|
|
Model made on the CNC milling machine |
Model printed on 3D printer |
Material: |
Aluminium PA6 |
PLA |
Processing time: |
2h |
4h 24min |
Cost of the model: |
317,90 zł |
78,28 zł |
Costs of the device
Many companies decide to outsource the execution of individual elements to external subcontractors. It is a good solution because a CNC milling machine and the hiring of a service specialist may not pay back this investment in a short time. It is similar in the case of 3D printing - using this type of service in the situation of manufacturing elements on a very small-scale will certainly be much more optimal than buying a machine. However, it is worth noting that the costs of a CNC milling machine are up to 7 times higher compared to a 3D printer with a similar working area. That depends, among other things, on the industrial solutions used, as well as the size of the working area of the device.

.jpg)